Study examines Earth and Mars to determine how climate change affects the paths of rivers
The study examines Earth and Mars to determine how climate change affects the paths of rivers.
The study examines Earth and Mars to determine how climate change affects the paths of gutters In a new study published in Nature Geosciences, researchers, led by a Tulane University sedimentologist, excavated why the paths of mooching gutters change over time and how they could be affected by climate change
The study examines Earth and Mars to determine how climate change affects the paths of rivers.
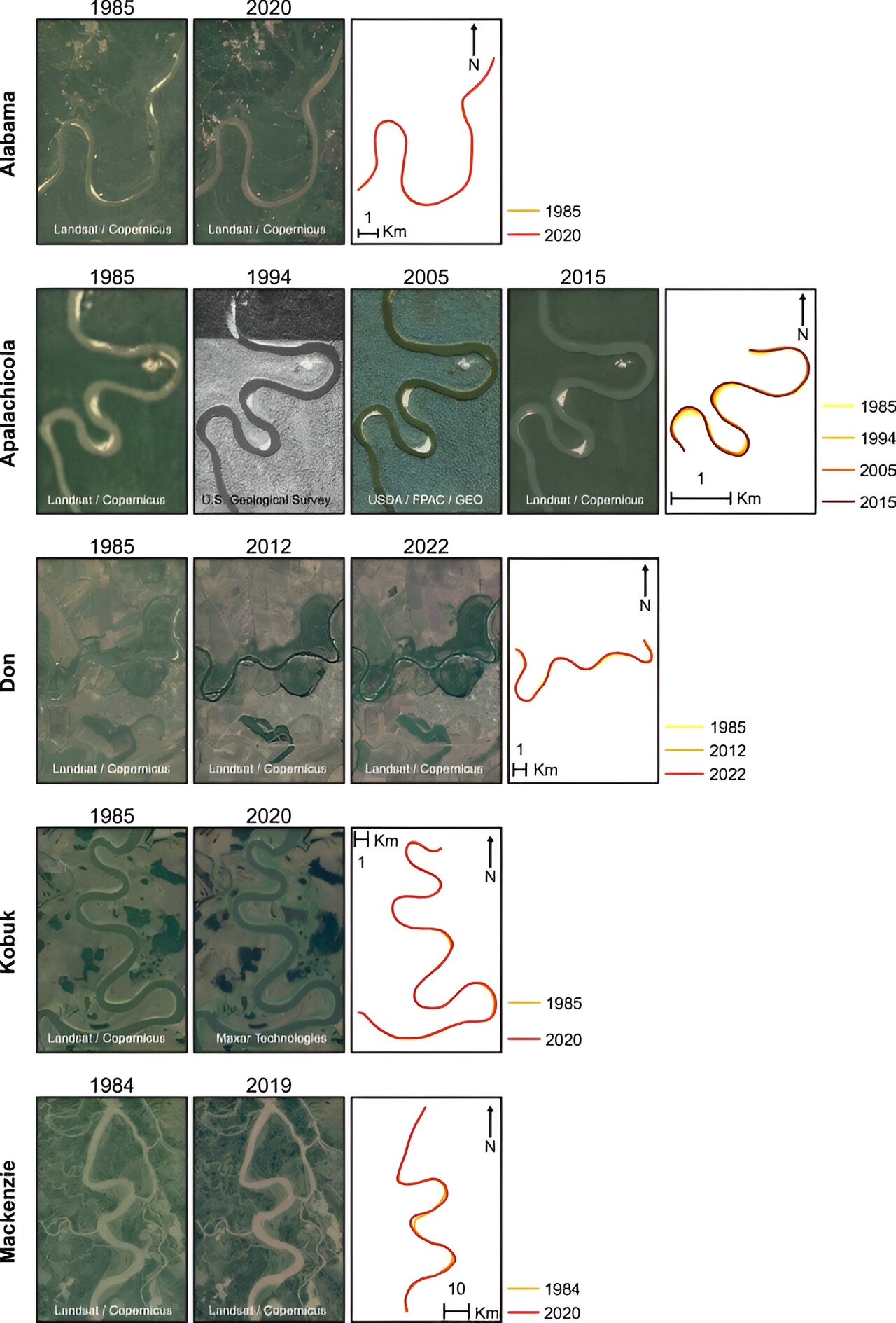
The study examines Earth and Mars to determine how climate change affects the paths of gutters In a new study published in Nature Geosciences, researchers, led by a Tulane University sedimentologist, excavated why the paths of mooching gutters change over time and how they could be affected by climate change. The study specifically looks at sluice sinuosity, or how important gutters wind. The sinuosity of gutters changes over time, depending on the age of the sluice and environmental changes. Some of these changes include deposit and water force and beachfront leafage, all of which are affected by climate change. The study set up that sluice sinuosity is related to the changes in how important water flows through the sluice. Rivers have different water situations depending on environmental factors, like rush situations. The researchers looked at maps of the gutters on Earth over time by using nonfictional data from as early as the fifth century and images from as early as 1939. They used data from 21 mesa mooching gutters. For the ancient shells on Mars, they used previously linked ancient sluice channels from remote seeing data. The ancient shells on Mars, untouched by mortal influence, gave Wu and his team a system to test their suppositions on how the sluice systems migrated and what their sinuosity looked like by the time they dried up. Their analysis is also a step toward understanding what the hydroclimate on Mars was like when there was still superficial water." It really lays the foundation for more advanced motifs," Wu said," like, were the environmental conditions suitable for life on Mars?" After performing an analysis on the gutters, the researchers separated them into two order variables- sinuosity and constant-sinuosity. The variable- sinuosity gutters noway reached a steady state, meaning their sinuosities continue changing, and the constant- sinuosity gutters did reach a steady state, meaning their average sinuosity remained fairly constant. Of the 21 Earth gutters studied, 13, including the Mississippi River, had variable sinuosity, while eight had constant sinuosity. Understanding what factors affect the sinuosity of gutters will give researchers and engineers sapience into how to manage gutters in the future. It can help with sluice restoration, future structure systems, and flood tide drift operation. This insight can be invaluable in attempts to palliate the impacts of climate change. As further extreme downfall happens further constantly due to the goods of climate change, disquisition like Wu's will come indeed more important when it comes to guarding and helping populations who live near gutters. According to a 2019 study in the International Journal of Water Resources Development, half of the world's population lives in sluice basins, all of whom could be affected by future cataracts from extreme downfall events
Note: The study examining Earth and Mars in the context of climate change's effect on river paths underscores the intrinsic relationship between planetary climate fluctuations and river dynamics. The interconnectedness of rising temperatures, glacial melt, sediment transport, and altered river courses on both planets emphasizes the urgency of addressing climate change. As Earth grapples with unprecedented environmental shifts, the lessons derived from Martian river valleys further emphasize the need for collective global efforts to mitigate and adapt to the challenges posed by climate change.
Tag: Climate Change, River Dynamics, Earth, and Mars Comparison, Planetary Claimat Shifts, Glacial Melting, Sediment Transport, River Path Alterations, Climate-Induced Changes, Extreme Weather Events, Global Environment Challenges, Interdisciplinary Research, Planetary Geology, Environmental Impacts, Adaptation Strategies, Comparative Planetary Science, Sustainable Resource Management.