If you are interested in learning about
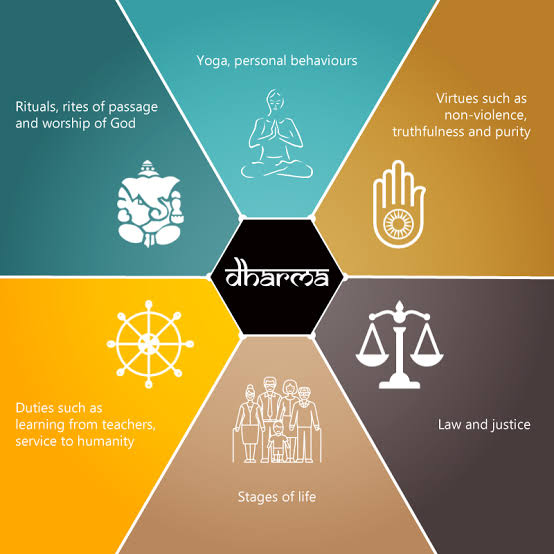

"Dharma" is a term that has various meanings across different contexts, especially in Eastern religions and philosophies. It originates from ancient Indian traditions, particularly Hinduism, Buddhism, Jainism, and Sikhism. The concept of dharma is complex and can be understood in different ways depending on the cultural and religious framework. In Hinduism, dharma refers to the moral and ethical duties, righteousness, and code of conduct that individuals must follow to lead a virtuous life. It encompasses duties and responsibilities based on one's age, gender, caste, occupation, and social role. Dharma is seen as the underlying principle that sustains the order and harmony in the universe. In Buddhism, dharma is used in several ways. One of the primary meanings is the teachings of the Buddha, which include the Four Noble Truths and the Eightfold Path, providing guidance on how to attain enlightenment and liberation from suffering. In this context, following the dharma means following the Buddha's teachings. In Jainism, dharma is a fundamental concept that refers to the moral and ethical principles guiding one's conduct. It includes principles of non-violence (ahimsa), truthfulness (satya), non-stealing (asteya), celibacy or chastity (brahmacharya), and non-possessiveness (aparigraha). In Sikhism, dharma is understood as the path of righteousness and devotion to God. It involves living a life of honesty, selfless service, and meditation on the divine. Overall, the concept of dharma emphasizes living in harmony with one's moral duties, spiritual path, and the greater cosmic order. It is a guiding principle for leading an ethical and meaningful life in various Eastern philosophical and religious traditions.

Table of Contents Introduction to Free Online Tools for PDF,...

Table of Contents How I Discovered Toolkhoj.com What Makes It...

महाशिवरात्रि के उपाय , बेर, काली मिर्च और धतूरे का...