Causes of diabetes and how to avoid
Diabetes is a chronic condition characterized by elevated blood sugar levels. There are two main types: type 1 and type 2 diabetes. Type 1 is caused by the immune system mistakenly attacking and destroying insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. It's not preventable and requires insulin treatment. Type 2 diabetes, however, is largely influenced by lifestyle factors. It's caused by insulin resistance, where cells don't respond properly to insulin. Genetics also play a role.
To avoid type 2 diabetes:
1. Maintain a healthy weight: Obesity increases the risk. Engage in regular physical activity and follow a balanced diet.
2. Eat well: Focus on whole grains, lean proteins, fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats. Limit sugary and processed foods.
3. Stay active: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise per week.
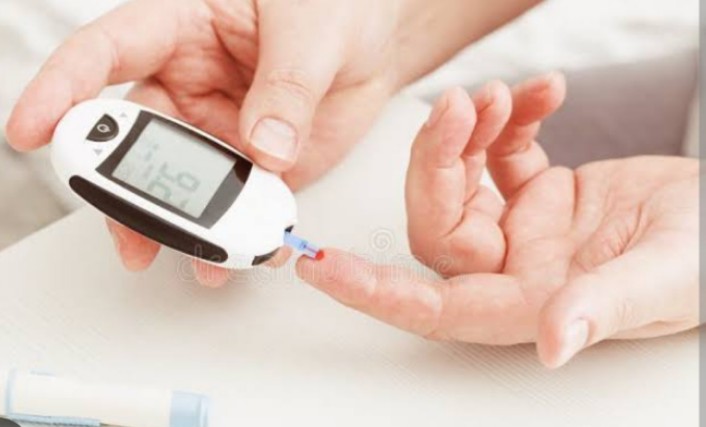
4. Monitor your blood sugar: Regular screenings help detect early signs of diabetes.
5. Manage stress: Chronic stress can contribute to diabetes. Practice relaxation techniques.
6. Get enough sleep: Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night.
7. Limit alcohol: If you drink, do so in moderation.
8. Avoid smoking: Smoking increases the risk of type 2 diabetes.
By adopting a healthy lifestyle, you can significantly reduce your risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Always consult a healthcare professional for personalized guidance.
Diabetes is a chronic medical condition that affects how your body processes glucose, a type of sugar used as a primary source of energy. There are two main types of diabetes: Type 1 and Type 2. Both types have different causes and risk factors. While Type 1 diabetes is primarily an autoimmune condition where the immune system attacks and destroys insulin-producing cells in the pancreas, Type 2 diabetes is more closely linked to lifestyle factors and genetics. In this essay, we will explore the causes of diabetes, with a specific focus on Type 2 diabetes, and discuss strategies to prevent its onset.
Causes of Diabetes:
1. Type 1 Diabetes:
Type 1 diabetes, often diagnosed in childhood or adolescence, occurs when the immune system mistakenly targets and destroys insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. Genetic predisposition and certain environmental triggers, such as viral infections, are believed to play a role in this autoimmune response.
2. Type 2 Diabetes:
Type 2 diabetes, which typically develops in adulthood, is strongly linked to lifestyle factors and genetics. The main underlying cause is insulin resistance, where the body's cells become less responsive to insulin, a hormone that helps regulate blood sugar levels. This leads to elevated blood sugar levels. Several factors contribute to the development of Type 2 diabetes:
Obesity:
Excess body weight, particularly abdominal fat, increases the risk of insulin resistance. Adipose tissue releases inflammatory chemicals that interfere with insulin signaling.
Physical Inactivity:
Sedentary lifestyles contribute to weight gain and worsen insulin resistance. Regular physical activity improves insulin sensitivity and helps manage blood sugar levels.
Unhealthy Diet:
A diet high in refined carbohydrates, sugary foods, and saturated fats contributes to weight gain and insulin resistance. Diets rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats are recommended.
Genetics:
Family history of diabetes can increase the risk, but lifestyle choices play a significant role in whether these genetic predispositions are expressed.
Age:
The risk of Type 2 diabetes increases with age, especially after 45.
Gestational Diabetes:
Women who develop diabetes during pregnancy (gestational diabetes) are at a higher risk of developing Type 2 diabetes later in life.
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome
(PCOS):
PCOS, a hormonal disorder common among women of reproductive age, is associated with insulin resistance and an increased risk of Type 2 diabetes.
Prevention Strategies:
1.Maintain a Healthy Weight:
Losing excess weight and maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise can significantly reduce the risk of Type 2 diabetes.
2. Healthy Diet:
Focus on whole foods, high-fiber options, lean proteins, and good fats. Limit refined sugars, sugary beverages, and processed foods.
3. Regular Physical Activity:
Engage in regular exercise, including aerobic activities and strength training, to improve insulin sensitivity and support overall health.
4.Blood Sugar Monitoring:
If you have a family history of diabetes or other risk factors, regular blood sugar monitoring can help catch any abnormalities early.
5.Avoid Sedentary Lifestyle:
Reduce sitting time and aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity per week.
6.Stress Management:
Chronic stress can impact blood sugar levels. Practicing stress-reduction techniques like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing can be beneficial.
7. Adequate Sleep:
Prioritize getting 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night, as poor sleep can negatively affect insulin sensitivity.
8. Moderate Alcohol Consumption:
If you consume alcohol, do so in moderation. Excessive alcohol intake can contribute to insulin resistance and other health issues.
9. Regular Health Check-ups:
Routine medical check-ups can help monitor blood sugar levels, identify risk factors, and take preventive measures.
In conclusion, while Type 1 diabetes is primarily autoimmune in nature, Type 2 diabetes is largely influenced by lifestyle choices and genetic predisposition. Preventing Type 2 diabetes requires a holistic approach that includes maintaining a healthy weight, adopting a balanced diet, staying physically active, managing stress, and getting regular check-ups. By taking proactive steps to prevent the onset of Type 2 diabetes, individuals can lead healthier lives and reduce the burden of this chronic condition.